Functional annotation
Overview
Teaching: 30 min
Exercises: 30 minQuestions
We now know where our protein encoding sequences are located on the genome and what their amino acid sequence is, however, we do not know what their function in the phage is. To figure this out we will compare the by meta predicted protein sequences to the PHROG database using HHsuite.
First we have to download the HHsuite index from the PHROG website. The models in the index file only have an ID, like phrog_13, which is not informative by itself. Hence we also download the phrog_annot_v3.tsv to link the ID to annotations (e.g. terminase protein).
Downloading the phrog HH-suite and corresponding annotation table
Again make sure we are in ~/day3/, then run the code below
mkdir phrog
cd phrog
wget https://phrogs.lmge.uca.fr/downloads_from_website/phrog_annot_v3.tsv
wget https://phrogs.lmge.uca.fr/downloads_from_website/phrogs_hhsuite_db.tar.gz
tar -xvzf phrogs_hhsuite_db.tar.gz
cd ..
Annotated proteins
- How many phrog annotation did we download (see the tsv)?
Annotating the predicted proteins
Unfortunately we cannot just pass our default_proteins.faa to hhsuite (unlike hmmer search. We first have to create a FASTA file for each invidiual protein sequence to do this we will use seqkit.
cd prodigal_default
mkdir single_fastas
seqkit split -i -O single_fastas/ proteins.faa
Running hhblits on phrog
Now we can finally annotate the protein sequences! We have to be in the prodigal_default directory for this and the next step.
mkdir hhsearch_results
for file in single_fastas/*.faa; do base=`basename $file .faa`; echo "hhblits -i $file -blasttab hhsearch_results/${base}.txt -z 1 -Z 1 -b 1 -B 1 -v 1 -d ../phrog/phrogs_hhsuite_db/phrogs -cpu 1" ; done > all_hhblits_cmds.txt
parallel --joblog hhblits.log -j8 :::: all_hhblits_cmds.txt
HHblits
- For our search we use
hhblits, but we could have also usedhhsearch, what is the difference? (see the wiki)- You probably noticed the message “WARNING: Ignoring invalid symbol ‘*’, why is this happening?
Parsing the results
Now it is time to parse the results :) For each query (predicted protein) we grab the best match (from hhsearch_results), link the ID to the annotation (in phrog_annot_v3.tsv) and find the genomic location in our Prodigal output file (genes.txt). Get the Python script to do this from GitHub:
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rickbeeloo/day3-data/main/parse_hmm_single.py
python3 parse_hmm_single.py hhsearch_results/ hhsearch_results.txt ../phrog/phrog_annot_v3.tsv genes.txt
I also wrote a script that will visualize the gene annotation of two provided contigs using gggenes. You can find the script here.. Like before create a new Rscript and copy paste the code. The line df <- read.table(file.choose().... (line: x) will open a file dialog where you can choose the hhsearch_results.txt. Then run the while loop that will ask you to provide two contig identifiers. Just a unique part is sufficient, such as bin_01||F1M_NODE_1. I added the option to save to an output file in case of weird symbols again… For example it will produce a figure like this:
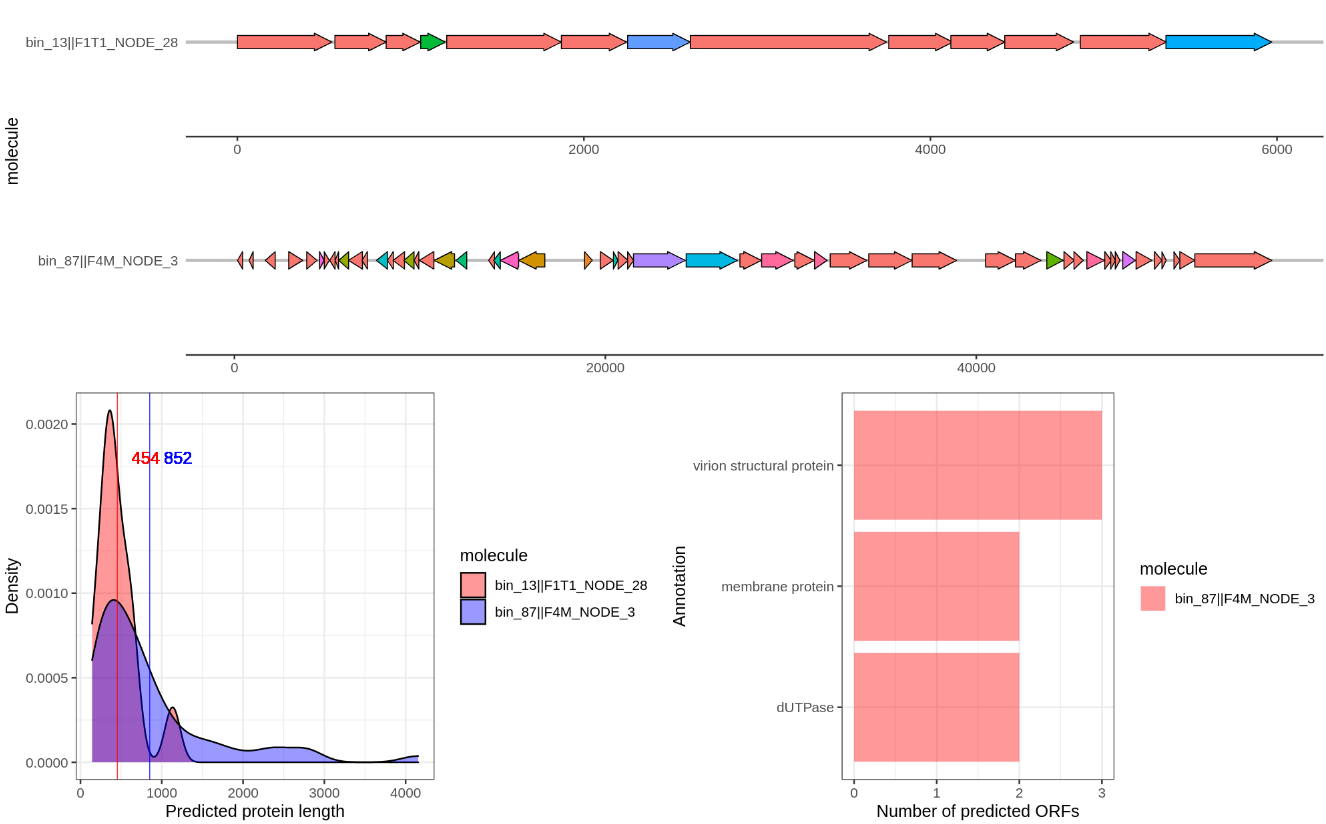
Compare several of the following contigs:
bin_87||F4M_NODE_3
bin_01||F1M_NODE_1
bin_62||F3M_NODE_2
bin_13||F1T1_NODE_28
HHblits
Take a closer look at the contigs
bin_01||F1M_NODE_1vsbin_62||F3M_NODE_2- both crassphages.
What do you notice in this comparison?
Go to Figure 7 of this paper, is this what you thought? How are we going to tackle this?
Annotating two contigs with a different translation table
In the paper a modified version of Prodigal is used. Instead of modifying Prodigal we will use translation table 15 where TAG is considered a coding codon instead of a STOP(*).
- How do we tell Prodigal to use this translation table? wiki
(NOTE: using a different translation table is not supported in meta mode, so we have to use the normal gene prediction here)
We have to go back to the ~/day3/ directory and then run the following
mkdir prodigal_dif_table
cd prodigal_dif_table
touch two_contigs.fasta
cat ../fasta_bins/bin_01.fasta > two_contigs.fasta
cat ../fasta_bins/bin_62.fasta >> two_contigs.fasta
prodigal -i two_contigs.fasta -a two_contig_proteins.faa -o two_contig_genes.txt -f sco -g 15
mkdir single_fastas
seqkit split -i -O single_fastas/ two_contig_proteins.faa
mkdir hhsearch_results
for file in single_fastas/*.faa; do base=`basename $file .faa`; echo "hhblits -i $file -blasttab hhsearch_results/${base}.txt -z 1 -Z 1 -b 1 -B 1 -v 1 -d ../phrog/phrogs_hhsuite_db/phrogs -cpu 1"; done > all_hhblits_cmds.txt
parallel --joblog hhblits.log -j8 :::: all_hhblits_cmds.txt
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rickbeeloo/day3-data/main/parse_hmm_single.py
python3 parse_hmm_single.py hhsearch_results/ two_contig_hhsearch_results.txt ../phrog/phrog_annot_v3.tsv two_contig_genes.txt
Use the script from the previous step (this time loading the two_contig_hhsearch_results) and again visualize the contigs bin_01||F1M_NODE_1 vs bin_62||F3M_NODE_2.
Compare predictions
- How did the prediction change? and what about
bin_01||F1M_NODE_1?
Key Points