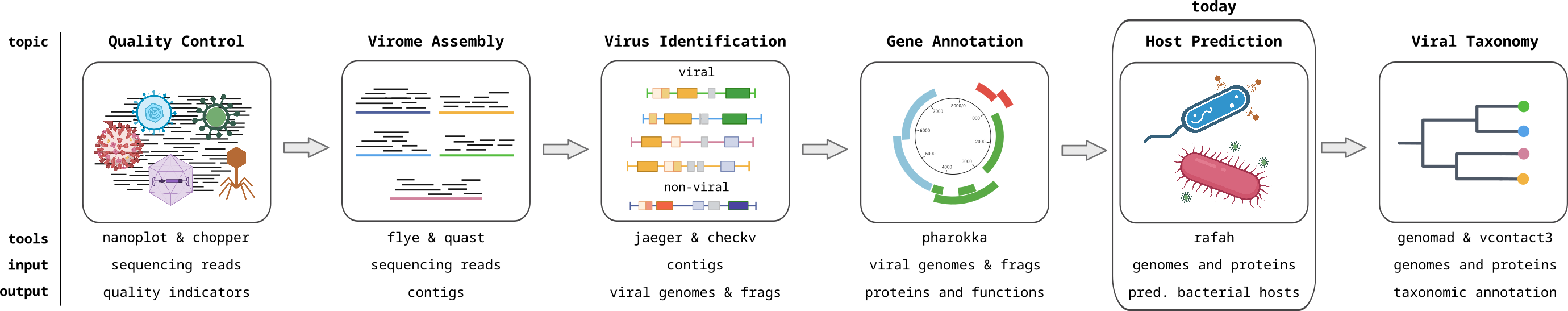
Host Prediction I
Overview
Teaching: 60 min
Exercises: 120 minObjectives
Understand how biological information is used to predict hosts
Understand the difficulties with host prediction
Learn about the new techniques that are being used for host prediction
Host prediction lecture
Listen to lecture by Varada and Malte (pay attention!!!) slides for host prediction
Questions
- What are some biological interactions viruses have with their hosts? (hint: start with the infection cycle)
Pick one classical host prediction method:
- In brief, explain how this works
- What is the major challenge with this method?
- How can you be confident in your host prediction?
- Evaluate the following scenarios: a) Two viral contigs match to the same host during the host prediction b) One viral contig matches 2 hosts: s__Salinibacter ruber and s__Longimonas halophila
For the hands-on part - we will be using a tool called RaFAH. This tool uses random forest model machine learning models to predict hosts for phages. They train the ML model using the protein content of viral sequences and compare it with manually curated classical host predictions (CRISPR sequences, tRNA and homology based matches) and related other tools. Have a look into the RaFAH paper and focus on the introduction and Figures 1 and 2.
Questions
- Briefly discribe how RaFAH derives its predictions from a genome sequence.
RaFAH produces a probability score for each host genus in its training set and reports the genus with the maximum probability. In Figure 2, you can find how this score relates to precision and recall for the test dataset the authors used.
- Decide, which probability score you would use as a cutoff for predictions you would trust. Explain your decision.
Additional resources
- IBM link on Random Forest (RF): introduces RF and decision trees in a short and simple way
- Chapter on RF for Bioinformatics: explains how RF measures feature importance and describes Bioinformatic applications
- Chapter on Decision Trees and RF: describes decision trees and RF by direct application in python. Also, if you want a great introduction to machine learning in general and python programming, take a look at the whole book by Jake VanderPlas, which is freely available online
Key Points